Table of Contents
1. Understanding Present Continuous Tense
The Present Continuous Tense, also known as the Present Progressive Tense, is a grammatical tense used to describe actions that are happening at the moment of speaking or are currently in progress. It is also used to describe temporary actions or situations that are occurring around the present time.
In English, the present continuous tense is formed using the present tense of the verb “to be” (am, is, are) followed by the base form of the main verb plus the “-ing” suffix.
For example:
– Action happening at the moment of speaking.
Example: “She is reading a book.”
– Action currently in progress.
Example: “They are watching TV right now.”
– Temporary action occurring around the present time.
Example: “I am studying for my exam this week.”
– The present continuous tense can also be used to describe future plans or arrangements when accompanied by a future time expression.
Example: “We are meeting our friends for dinner tomorrow.” (Future plan expressed in the present continuous tense.)
Overall, the present continuous tense is used to indicate actions or situations that are happening now, around the present time, or as future plans.
2. Forming Present Continuous Tense
The three forms of the Present Continuous Tense are used to construct sentences in different ways to convey actions or situations that are happening at the moment of speaking or around the present time. Here’s what each form means:
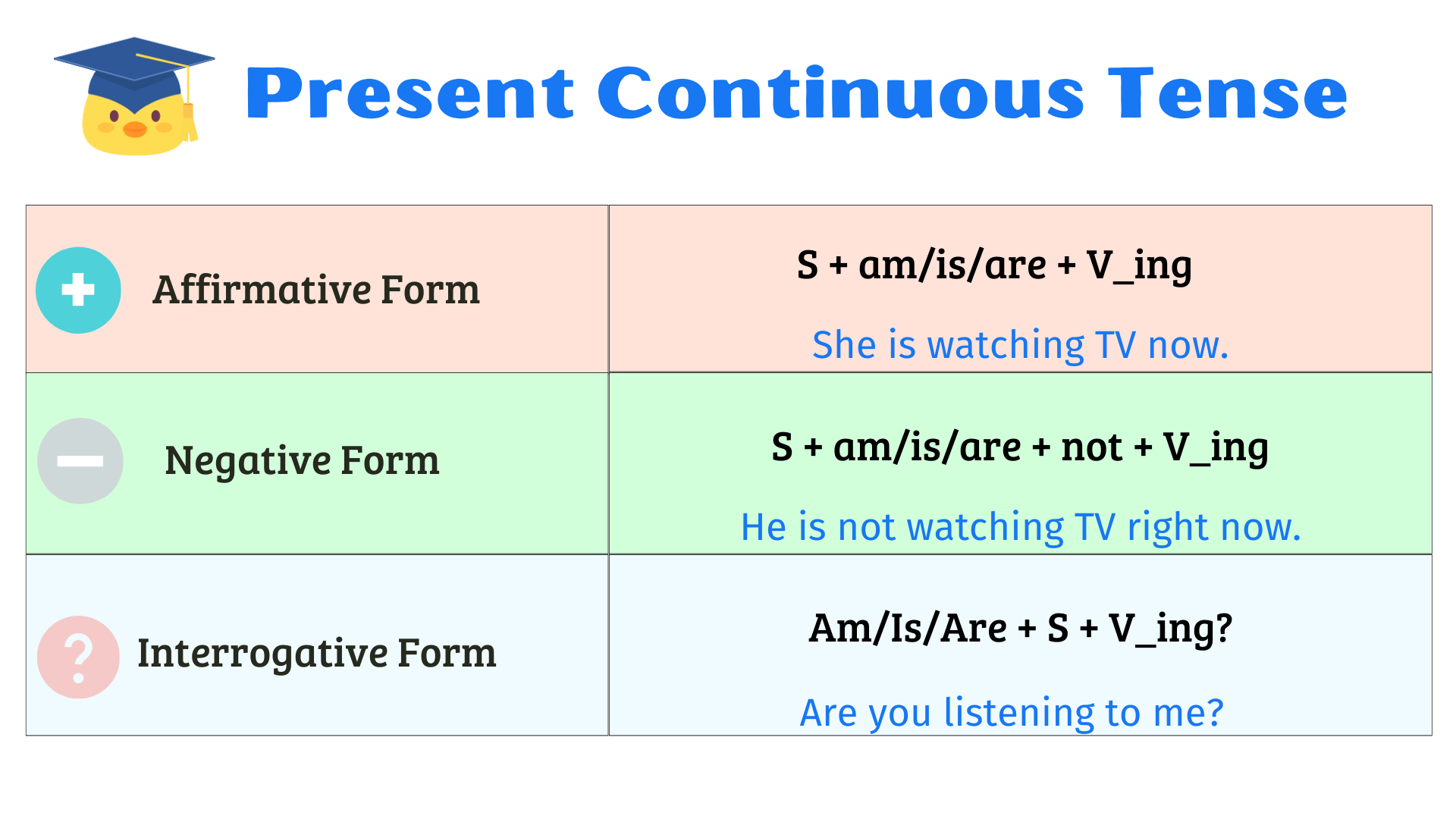
2.1 (+) Affirmative:
The affirmative form of the Present Continuous Tense is used to state that an action is currently happening or a situation is currently occurring. It is formed using the present tense of the verb “to be” (am, is, are) followed by the base form of the main verb plus the “-ing” suffix.
For example:
“She is watching TV.” (Affirmative statement indicating that she is currently watching TV.)
“They are studying for their exams.” (Affirms that they are currently engaged in studying for their exams.)
“The children are playing in the garden.” (Affirms that the children are currently engaged in playing in the garden.)
“She is cooking dinner for her family.” (Affirms that she is currently engaged in cooking dinner for her family.)
“I am typing an email to my friend.” (Affirms that I am currently engaged in typing an email to my friend.)
2.2 (-) Negative:
The negative form of the Present Continuous Tense is used to state that an action is not currently happening or a situation is not currently occurring. It is formed by adding the word “not” after the present tense of the verb “to be” (am not, is not, are not).
For example:
“They are not playing outside.” (Negative statement indicating that they are not currently playing outside.)
“He is not watching TV right now.” (States that he is currently not engaged in watching TV.)
“They are not listening to music at the moment.” (States that they are currently not engaged in listening to music.)
“She is not wearing her glasses today.” (States that she is currently not wearing her glasses.)
“We are not going to the movies tonight.” (States that we are currently not planning to go to the movies tonight.)
2.3 (?) Interrogative:
The interrogative form of the Present Continuous Tense is used to ask questions about actions or situations that are currently happening or occurring around the present time. It is formed by inverting the present tense of the verb “to be” (am, is, are) with the subject. For example:
– “Is she cooking dinner?” (Interrogative question asking if she is currently cooking dinner.)
– “Are you listening to me?” ( Asks whether “you” are currently engaged in listening.)
– “Is she working on her project?” (Asks whether she is currently engaged in working on her project.)
– “Are they waiting for the bus?” (Asks whether they are currently engaged in waiting for the bus.)
– “Am I pronouncing it correctly?” (Asks whether I am currently pronouncing it correctly.)
In summary, the affirmative form affirms actions or situations currently happening, the negative form negates actions or situations currently happening, and the interrogative form asks questions about actions or situations currently happening or occurring around the present time using the Present Continuous Tense.
3. Recognizing signal words for the Present Continuous tense
To recognize the Present Continuous tense in English sentences, you can look for several key indicators:
- Verb Forms: The main verb in the Present Continuous tense is formed by using the present tense of the verb “to be” (am, is, are) followed by the base form of the main verb plus the “-ing” suffix. For example:
“She is reading a book.”
“They are watching TV right now.”
- Time Expressions: The Present Continuous tense is often used with time expressions that indicate actions or situations happening around the present moment. These expressions include “at the moment,” “right now,” “currently,” “this week/month/year,” etc. For example:
“I am studying for my exam this week.”
“They are traveling to Europe at the moment.”
- Contextual Clues: Pay attention to the context of the sentence. If the sentence describes an action or situation that is currently happening or in progress, it is likely in the Present Continuous tense. For example:
“She is talking on the phone.”
“He is working on a project.”
- Use of “-ing” Form: The presence of the “-ing” form of the main verb is a clear indication of the Present Continuous tense. For example:
“They are playing soccer in the park.”
“I am writing an email to my friend.”
By paying attention to these indicators and contextual clues, you can easily recognize when the Present Continuous tense is being used in English sentences.